Barometric Pressure
Barometric Pressure
Barometric pressure is also referred to as “atmospheric pressure” and is simply the force that is created by the weight of the air. It is determined by the temperature and movement of the atmosphere and can cause both high and low pressure. It is suggested that fish behavior is influenced by changes in barometric pressure. While barometric pressure may not directly affect fishing conditions, it is a major factor that can influence what a fish may be doing at any given time.
I. Introduction
Definition of barometric pressure
Barometric pressure, also known as atmospheric pressure, is the force exerted by the weight of the atmosphere on the Earth’s surface. It is measured in units of pressure, such as millibars or inches of mercury. High- and low-pressure systems are created by the movement and temperature of the atmosphere and can affect weather conditions.
Importance of barometric pressure in fishing
Barometric pressure is important in fishing because it can affect fish behavior. Many anglers believe that changes in barometric pressure can influence the feeding patterns and activity levels of fish. For example, some anglers have observed that fish tend to feed more actively during periods of stable or slowly rising barometric pressure, while they may become less active during periods of rapidly falling pressure. Understanding the effects of barometric pressure on fish behavior can help anglers improve their chances of success when fishing.
II. Understanding Barometric Pressure
High- and low-pressure systems
High- and low-pressure systems are large masses of air that have different pressure characteristics. High pressure systems are associated with sinking air and bring clear skies and calm weather. Low pressure systems, on the other hand, are associated with rising air and can bring clouds, precipitation, and stormy weather.
These systems are created by the movement and temperature of the atmosphere. Air tends to flow from areas of high pressure to areas of low-pressure, which can cause weather patterns to change. For example, as a low-pressure system moves into an area, it can bring clouds and precipitation. As it moves away and is replaced by a high-pressure system, the weather may clear up.
High- and low-pressure systems can also affect fishing conditions. Some anglers have observed that fish tend to be more active during periods of stable or slowly rising barometric pressure, which is often associated with high-pressure systems. During periods of rapidly falling pressure, which can occur as a low-pressure system moves in, fish may become less active.
How barometric pressure is measured
Barometric pressure is measured using an instrument called a barometer. There are two main types of barometers: mercury and aneroid.
A mercury barometer measures atmospheric pressure by balancing the weight of a column of mercury against the weight of the air pressing down on a reservoir of mercury. As the air pressure changes, the height of the mercury column changes, indicating the change in pressure.
An aneroid barometer, on the other hand, uses a small, flexible metal box called an aneroid cell to measure changes in air pressure. As the air pressure changes, the walls of the aneroid cell expand or contract, causing a needle on the face of the barometer to move and indicate the change in pressure.
Barometric pressure is typically measured in units of pressure such as millibars or inches of mercury.
III. Effects of Barometric Pressure on Fish Behavior
Fish activity during high- and low-pressure systems
Fish activity can be affected by changes in barometric pressure, which are often associated with high- and low-pressure systems. Many anglers have observed that fish tend to be more active during periods of stable or slowly rising barometric pressure, which is often associated with high pressure systems. During these periods, fish may feed more actively and be more likely to take bait.
On the other hand, during periods of rapidly falling pressure, which can occur as a low-pressure system moves in, fish may become less active. They may move to deeper water or seek cover and be less likely to feed. Some anglers believe that this is because the rapid change in pressure can make fish feel uncomfortable.
It is important to note that these are general observations, and that fish behavior can vary depending on many factors, including the species of fish, the time of year, and the specific body of water.
Smaller fish are more sensitive to changes in barometric pressure. When the pressure drops, they often seek deeper waters to alleviate discomfort. In addition to changing their location, their eating habits may also be affected by changes in pressure.
Fish in general feel the changes in barometric pressure via their air bladders, also known as swim bladders. These organs are inflated air sacs that help fish maintain their buoyancy. When the barometric pressure goes down, the air bladder will inflate to accommodate for the lessened pressure.
How fish respond to changes in barometric pressure
Fish can respond to changes in barometric pressure in a variety of ways. Many anglers believe that changes in barometric pressure can influence the feeding patterns and activity levels of fish.
For example, during periods of stable or slowly rising barometric pressure, fish may feed more actively and be more likely to take bait. This may be because the stable conditions make fish feel more comfortable and willing to feed.
On the other hand, during periods of rapidly falling pressure, fish may become less active. They may move to deeper water or seek cover and be less likely to feed. Some anglers believe that this is because the rapid change in pressure can make fish feel uncomfortable.
It is important to note that these are general observations, and that fish behavior can vary depending on many factors, including the species of fish, the time of year, and the specific body of water.
IV. Using Barometric Pressure to Improve Fishing Success
Tips for fishing during different barometric pressures
- During periods of stable or slowly rising barometric pressure, fish may feed more actively. Try using live bait or lures that mimic the natural prey of the fish you are targeting.
- During periods of rapidly falling pressure, fish may become less active and move to deeper water or seek cover. Try fishing in deeper water or near structure where fish may be hiding.
- Pay attention to changes in weather conditions, as these can affect barometric pressure and fish behavior. For example, an approaching storm front can cause a rapid drop in pressure and may affect fish activity.
- Keep track of barometric pressure and fish activity over time to learn how the fish in your area respond to changes in pressure. This can help you plan your fishing trips and improve your chances of success.
- Remember that barometric pressure is just one factor that can affect fish behavior. Other factors such as water temperature, time of year, and food availability can also play a role.
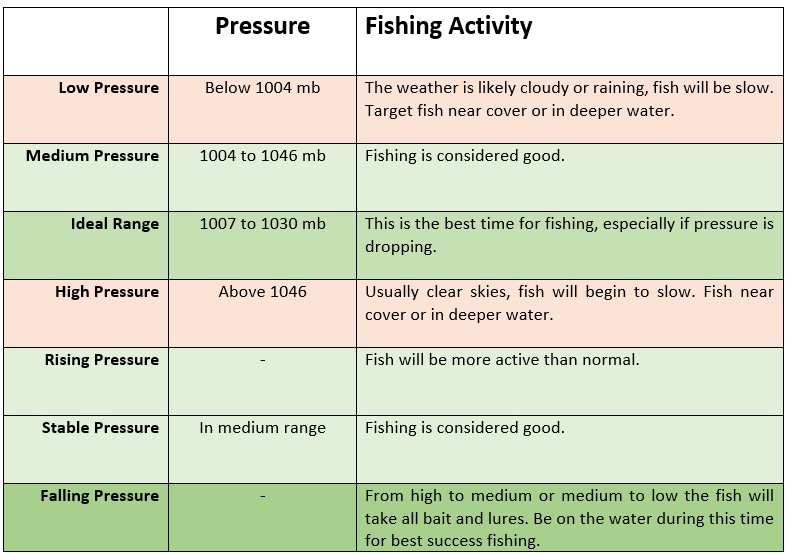
Here are some ways to track and use barometric pressure information to improve your fishing success
- Use a barometer: You can purchase a barometer to measure the barometric pressure at your fishing location. This will allow you to track changes in pressure in real-time and adjust your fishing strategy accordingly.
- Check weather reports: Many weather reports include information on barometric pressure. You can use this information to plan your fishing trips and choose the best times to fish based on the predicted pressure conditions.
- Keep a fishing log: Record the date, time, location, weather conditions, and barometric pressure for each of your fishing trips. Also, record information on fish activity and your catch rate. Over time, this information can help you identify patterns and learn how fish in your area respond to changes in barometric pressure.
- Use technology: There are many smartphone apps and websites that provide real-time barometric pressure information for specific locations. You can use these tools to track changes in pressure and plan your fishing trips accordingly.
Remember that barometric pressure is just one factor that can affect fish behavior. Other factors such as water temperature, time of year, and food availability can also play a role.
V. Conclusion
Key factors to consider when it comes to barometric pressure and freshwater fishing
- Changes in barometric pressure: Many anglers believe that changes in barometric pressure can influence fish behavior. For example, fish may feed more actively during periods of stable or slowly rising pressure, while they may become less active during periods of rapidly falling pressure.
- High- and low-pressure systems: High- and low-pressure systems can affect weather conditions and fish behavior. High pressure systems are associated with clear skies and calm weather, while low pressure systems can bring clouds, precipitation, and stormy weather.
- Tracking barometric pressure: Keeping track of changes in barometric pressure can help you plan your fishing trips and improve your chances of success. You can use a barometer, check weather reports, or use technology to track changes in pressure.
- Other factors: Remember that barometric pressure is just one factor that can affect fish behavior. Other factors such as water temperature, time of year, and food availability can also play a role.
- Importance of considering barometric pressure when fishing
In conclusion, considering barometric pressure when fishing can be important because it can affect fish behavior. Many anglers believe that changes in barometric pressure can influence the feeding patterns and activity levels of fish. By understanding the effects of barometric pressure on fish behavior and tracking changes in pressure, anglers can improve their chances of success when fishing. However, it is important to remember that barometric pressure is just one factor that can affect fish behavior and other factors such as water temperature, time of year, and food availability should also be considered.